What Is Not A Function Of Proteins: A Comprehensive Guide To Understanding Protein Roles
Proteins are essential macromolecules that play a vital role in various biological processes. However, not all biological activities are directly influenced by proteins. Understanding what is not a function of proteins can provide a clearer picture of how these molecules operate within the human body and other organisms. This article will delve into the specifics of protein functions and highlight the activities that proteins do not perform.
Proteins are often referred to as the "workhorses" of the cell due to their diverse roles in maintaining life. They are involved in everything from catalyzing biochemical reactions to providing structural support. Yet, there are limits to their capabilities. By exploring these limits, we can better appreciate the complexity of biological systems and the roles played by other molecules such as carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids.
In this article, we will examine the various functions of proteins, identify what is not a function of proteins, and provide valuable insights into their roles in biological processes. Whether you're a student, researcher, or simply curious about biology, this guide will provide you with the information you need to understand protein functionality.
- Woman Spring Jacket
- Mother Daughter Dresses Matching
- Tasman X Uggs
- What Is The Door Test
- Shades Of Ash Blonde
Table of Contents
- The Roles of Proteins
- What Is Not a Function of Proteins?
- Protein Structure and Function
- Enzymatic Activity
- Structural Support
- Transport and Storage
- Cell Signaling
- Immunological Functions
- Energy Storage
- Genetic Information
- Conclusion
The Roles of Proteins
Proteins are fundamental to life, performing a wide array of functions within living organisms. These macromolecules are composed of amino acids linked by peptide bonds and can be found in every cell. Some of the primary functions of proteins include enzymatic activity, structural support, transport, and storage. However, proteins do not perform all biological functions.
Primary Functions of Proteins
Proteins serve as enzymes that catalyze biochemical reactions, structural components that provide strength and stability to cells, and signaling molecules that facilitate communication between cells. Additionally, they are involved in the transport and storage of molecules such as oxygen and iron. Despite these crucial roles, proteins are not responsible for certain biological activities, which we will explore in the following sections.
What Is Not a Function of Proteins?
While proteins are indispensable in many biological processes, they do not perform every function in the body. For instance, proteins are not responsible for storing genetic information, which is the role of nucleic acids such as DNA and RNA. Additionally, proteins do not serve as the primary energy source for most organisms, as this role is typically filled by carbohydrates and lipids.
- What Do You Call Your Partner When Engaged
- Slick Middle Part
- Sensoril Vs Ksm 66
- Ruhama Wolle
- Shoulder Length Black Hair With Layers
Key Non-Protein Functions
- Genetic information storage
- Primary energy storage
- Certain metabolic processes
Protein Structure and Function
The structure of a protein determines its function. Proteins can be classified into four levels of structure: primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary. The primary structure refers to the sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain, while the secondary structure involves local folding patterns such as alpha-helices and beta-sheets. The tertiary structure refers to the overall three-dimensional shape of a single polypeptide chain, and the quaternary structure describes the arrangement of multiple polypeptide chains in a multi-subunit protein.
Structure Dictates Function
The specific structure of a protein enables it to perform its designated function. For example, enzymes have an active site that is complementary in shape to their substrate, allowing them to catalyze specific reactions. However, proteins are not involved in processes that require non-protein molecules, such as the storage of genetic information in DNA.
Enzymatic Activity
One of the most well-known functions of proteins is their role as enzymes. Enzymes are proteins that increase the rate of chemical reactions by lowering the activation energy required for the reaction to occur. They are highly specific, meaning that each enzyme typically catalyzes only one type of reaction or works with a specific substrate.
Limitations of Enzymatic Activity
Despite their efficiency, enzymes cannot perform all types of chemical reactions. For example, they are not involved in the synthesis of DNA from RNA, a process that requires the action of ribozymes, which are RNA molecules with catalytic activity.
Structural Support
Proteins such as collagen and keratin provide structural support to tissues and organs. Collagen is the most abundant protein in the human body and is a major component of connective tissues such as tendons, ligaments, and skin. Keratin, on the other hand, is found in hair, nails, and the outer layer of skin.
Non-Protein Structural Components
While proteins are essential for structural support, other molecules such as lipids and carbohydrates also play important roles. For example, lipids are a major component of cell membranes, providing a barrier between the inside and outside of the cell. Carbohydrates, in the form of glycogen, are stored in the liver and muscles for energy.
Transport and Storage
Proteins are involved in the transport and storage of various molecules within the body. Hemoglobin, for example, is a protein that transports oxygen from the lungs to tissues and removes carbon dioxide from tissues to the lungs. Ferritin is another protein that stores iron in the liver, preventing toxicity from excess iron in the bloodstream.
Non-Protein Transporters
Although proteins are crucial for transport and storage, other molecules such as lipoproteins and lipids also play a role. Lipoproteins, for instance, transport cholesterol and triglycerides through the bloodstream, while lipids store energy in the form of fat.
Cell Signaling
Proteins are involved in cell signaling, a process by which cells communicate with one another. Hormones such as insulin and growth factors are protein-based signaling molecules that regulate metabolism and growth, respectively. Receptors on the surface of cells recognize these signaling molecules and initiate a cascade of events within the cell.
Non-Protein Signaling Molecules
While proteins are important for cell signaling, other molecules such as lipids and nucleotides also play a role. For example, nitric oxide (NO) is a gas molecule that acts as a signaling molecule in the cardiovascular system, regulating blood pressure and blood flow.
Immunological Functions
Proteins are essential for the immune system, which protects the body from pathogens such as bacteria and viruses. Antibodies, which are proteins produced by B cells, recognize and bind to specific antigens, marking them for destruction by other immune cells. Complement proteins also play a role in the immune response by enhancing the ability of antibodies and phagocytic cells to clear microbes and damaged cells.
Non-Protein Immune Components
Although proteins are critical for the immune response, other molecules such as carbohydrates and lipids also contribute. For example, glycoproteins on the surface of cells can act as receptors for pathogens, while lipids are involved in the formation of the cell membrane, which provides a barrier against invasion.
Energy Storage
Proteins are not the primary source of energy storage in most organisms. Instead, carbohydrates and lipids serve this role. Glycogen, a polysaccharide stored in the liver and muscles, is the primary form of energy storage in humans. Lipids, in the form of triglycerides, are stored in adipose tissue and provide a more concentrated source of energy.
Protein as an Energy Source
While proteins can be used as an energy source during periods of starvation or intense physical activity, this is not their primary function. The breakdown of proteins for energy is less efficient than the breakdown of carbohydrates and lipids, making them a secondary energy source.
Genetic Information
Proteins do not store genetic information. This role is fulfilled by nucleic acids such as DNA and RNA. DNA contains the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all living organisms, while RNA plays a role in protein synthesis and gene regulation.
The Role of Nucleic Acids
Nucleic acids are essential for the storage and transmission of genetic information. DNA provides the blueprint for the synthesis of proteins, while RNA acts as an intermediary molecule in the process of protein synthesis. Proteins, on the other hand, are the products of gene expression and do not store genetic information.
Conclusion
In conclusion, proteins are vital macromolecules that perform a wide range of functions in living organisms. However, they do not perform every biological function. Understanding what is not a function of proteins can provide a more comprehensive view of biological systems and the roles played by other molecules such as carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids.
We encourage you to explore further topics related to proteins and their functions. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to leave them below. Additionally, consider sharing this article with others who may find it informative. For more insights into biology and related fields, explore our other articles on the site.
Data and references for this article were sourced from reputable scientific journals and publications, including:
- Group Gift For Kids
- Petite With Big Breasts
- Shoulder Length Black Hair With Layers
- Vivaia Discount
- Christina Applegate House
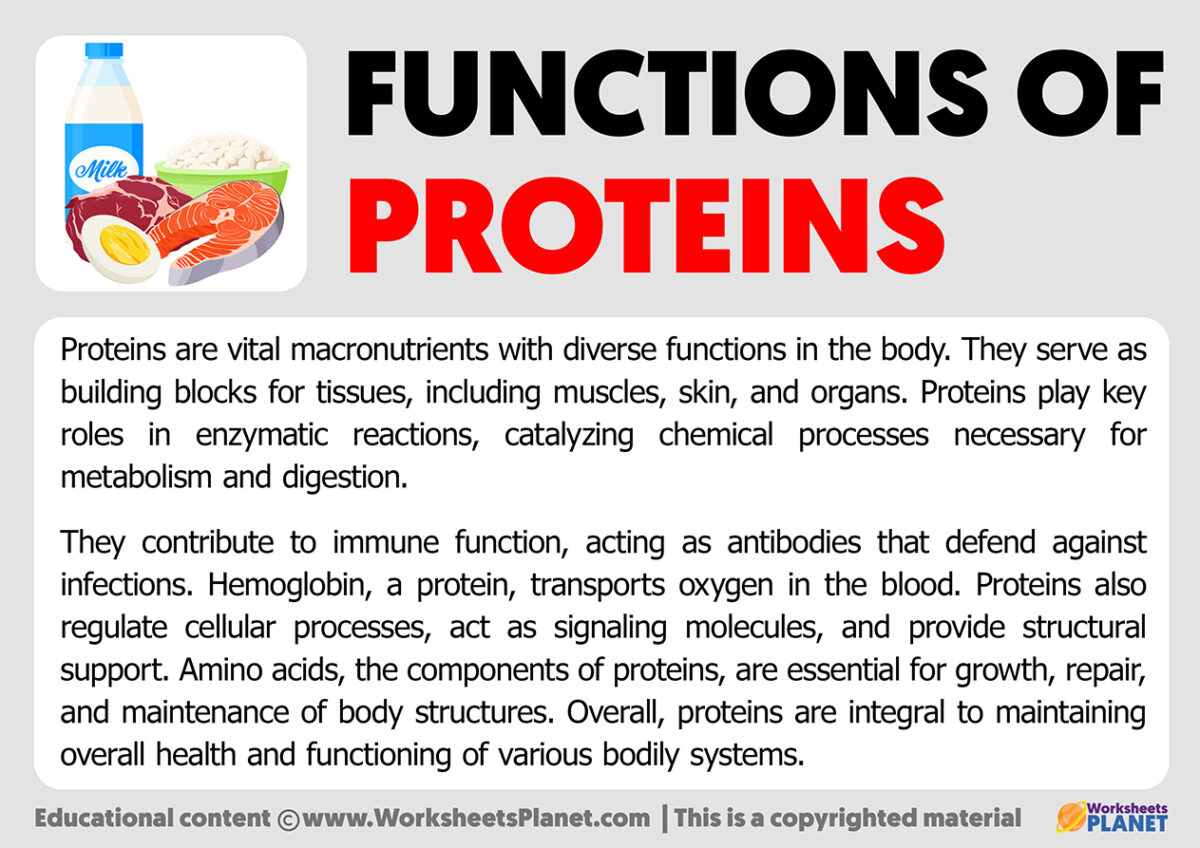
Function of Proteins
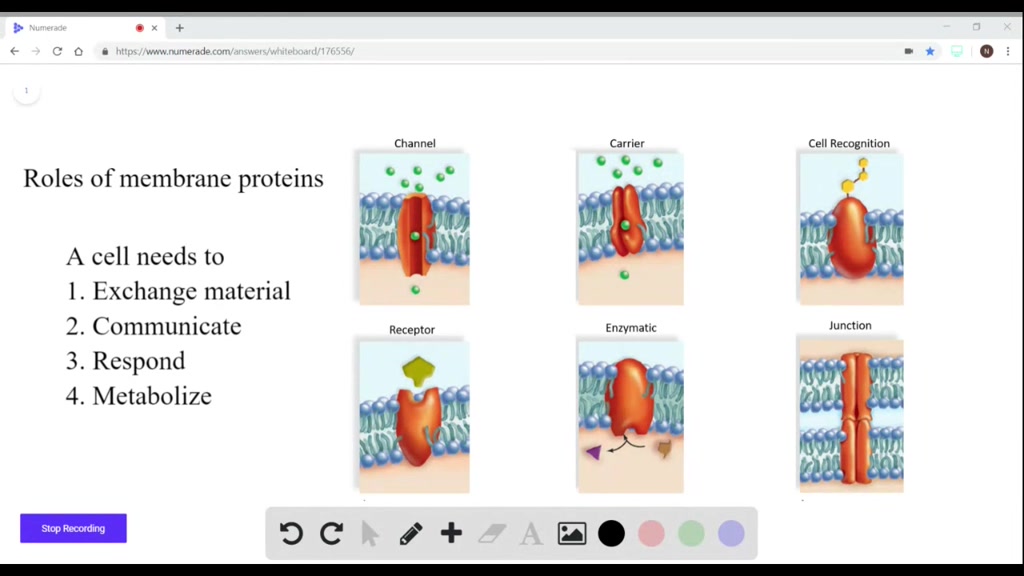
SOLVED Which of the following is not a function of proteins present in
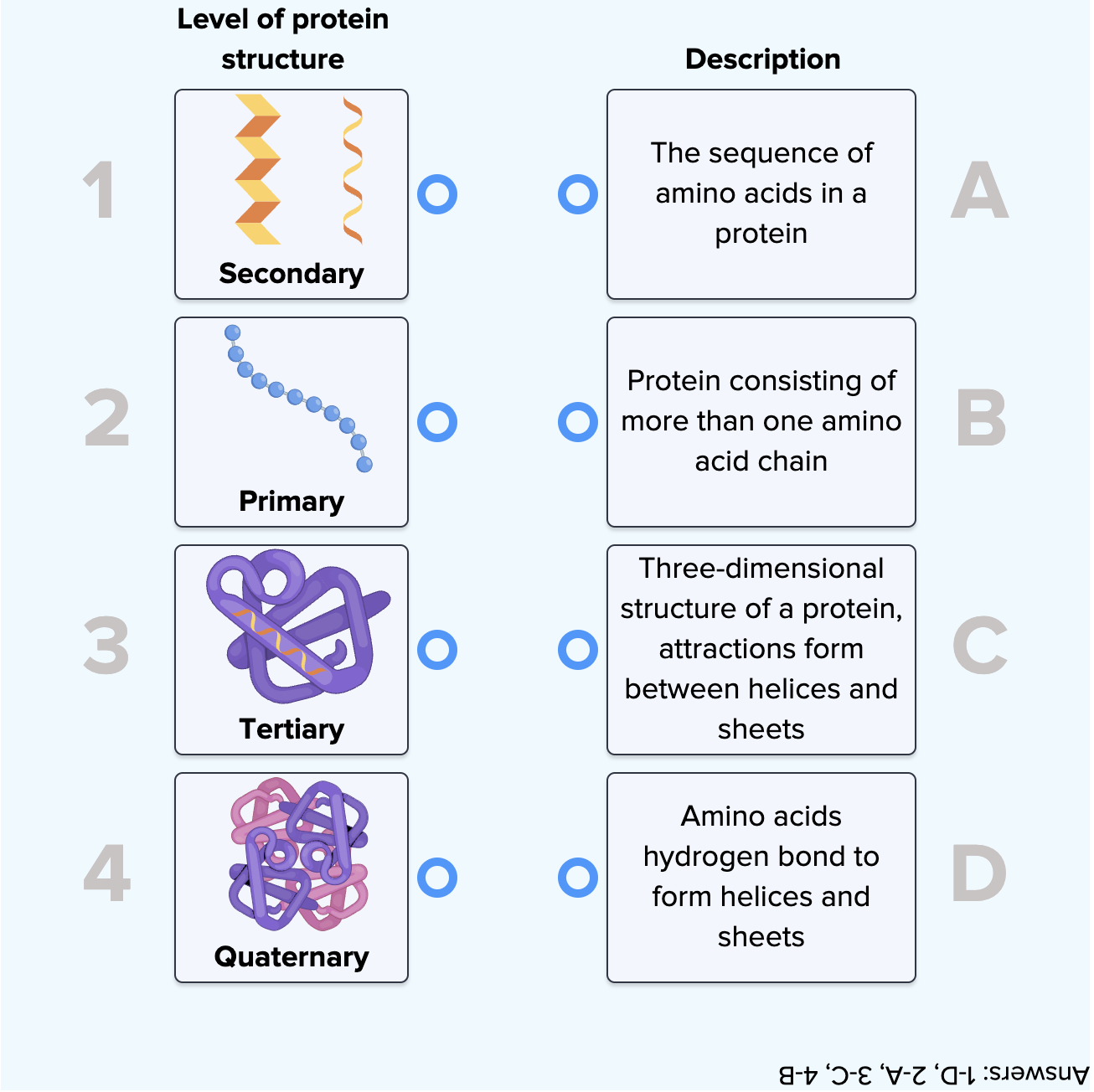
Proteins Structure